Strategic Planning Models
Strategic planning models are frameworks that help organizations define their strategy and make decisions to achieve their long-term goals. Here are some of the most popular strategic planning models:
1. Basic Model
This model is ideal for organizations new to strategic planning. It involves defining the mission, vision, goals, and action plans. It’s straightforward and helps establish a clear direction1.
2. Issue-Based Model
Also known as the goal-based model, this approach focuses on identifying and addressing specific issues or goals. It typically involves a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to prioritize issues and develop strategies1.
3. Alignment Model
This model ensures that the organization’s structure and resources are aligned with its strategy. It helps in identifying gaps between the current state and the desired future state, ensuring all parts of the organization are working towards the same goals2.
4. Scenario Planning
This model involves creating different scenarios based on potential future events and developing strategies for each scenario. It’s useful for organizations operating in highly uncertain environments2.
5. Balanced Scorecard
Developed by Robert Kaplan and David Norton, this model translates an organization’s vision and strategy into a comprehensive set of performance measures. It balances financial and non-financial metrics across four perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth2.
6. Hoshin Kanri
Also known as Policy Deployment, this Japanese model focuses on aligning the organization’s strategic goals with its operational activities. It involves setting long-term objectives and breaking them down into annual goals and action plans2.
7. Blue Ocean Strategy
This model encourages organizations to create new market spaces (blue oceans) rather than competing in existing ones (red oceans). It focuses on innovation and differentiation to make the competition irrelevant2.
8. OKRs (Objectives and Key Results)
Popularized by companies like Google, OKRs involve setting clear, measurable objectives and tracking progress through key results. This model promotes alignment, transparency, and accountability2.
9. McKinsey 7S Model
This model examines seven internal elements of an organization (strategy, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff, and skills) to ensure they are aligned and mutually reinforcing2.
10. Ansoff Matrix
This model helps organizations decide their growth strategy by focusing on existing or new markets and products. It includes four strategies: market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification2.
Each model has its strengths and is suited to different types of organizations and situations. Would you like to explore any of these models in more detail or discuss how to apply them to your organization?
positioning strategy
portfolio analysis in strategic management
strategic business analysis
differentiation focus strategy
smart strategy
ideation techniques
strategic management model
gap analysis in strategic management
lean strategy
strategy planning and operation
strategic control
techniques of controlling
conflict resolution strategies
creating shared value
In this article, we’ll explore five key elements of the strategy framework.
Marketing Flamework
strategic portfolio management
5 C Marketing
Swot analysis in strategic management
Michael E. Porters Five Forces Analysis
Michael Porters 5 Forces Analysis is a strategic framework used to evaluate the competitive environment of an industry. It examines five key forces: competitive rivalry (the intensity of competition among existing firms), threat of new entrants (the ease with which new competitors can enter the market), bargaining power of suppliers (the influence suppliers have on prices and terms), bargaining power of buyers (the influence customers have on pricing and quality), and threat of substitutes (the availability of alternative products or services). This analysis helps businesses understand the factors affecting their industry’s profitability and develop strategies to enhance their competitive position.
michael porter strategy
porter analysis
porter 5 forces model
5 forces model
porters five forces model
porter strategy
porter five forces model
porter 5
Michael porter five forces analysis
porter forces
porter generic strategies
porter model
porters generic strategy
Strategic group analysis
Strategic group analysis (SGA) is a method used in strategic management and organizational economics to segment and assess industries. It helps organizations understand their competitive environment by identifying similar organizations and mapping their strategic characteristics.
New Business Planning
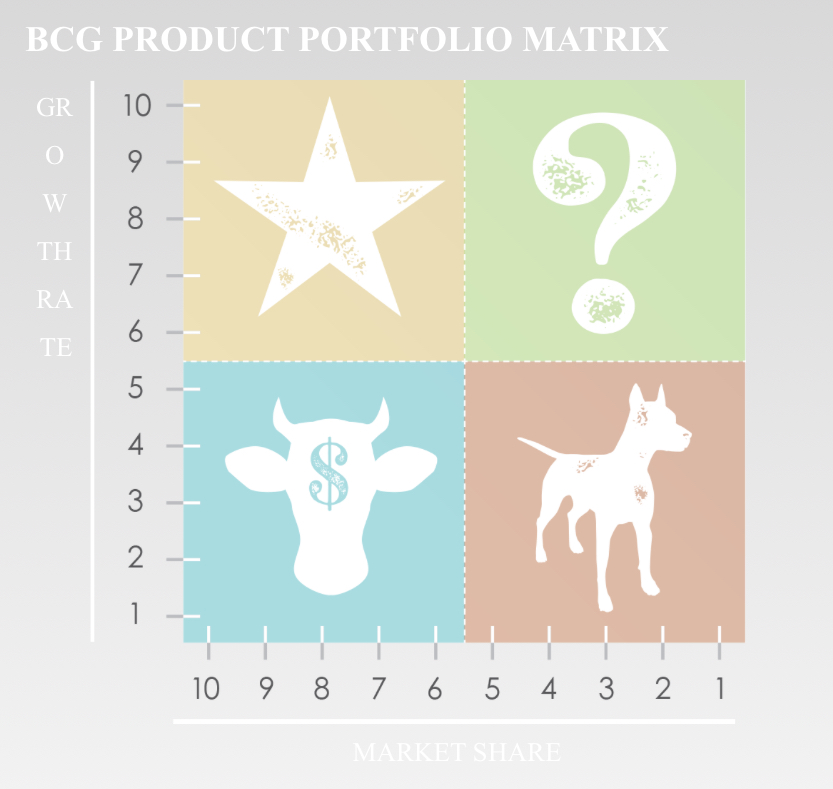
Product Portfolio Management Analysis
Definition: Product Portfolio Management Analysis is the process of systematically reviewing and managing a company’s collection of products. Its goal is to optimize the performance of each product while ensuring alignment with the company’s broader business objectives.
Summary: This analysis involves assessing the profitability, market position, and strategic fit of each product within the portfolio. By evaluating these factors, companies can make informed decisions on which products to invest in, develop further, or phase out, ultimately maximizing the overall value and effectiveness of their product offerings.
Product Portfolio Management Analysis is a strategic approach used to refine a company’s product range to maximize value and meet broader business goals. The process starts with an inventory assessment, which involves identifying and classifying all current products. This provides a detailed view of the product lineup and clarifies each product’s role within the portfolio.
Following this, a detailed performance analysis is carried out to evaluate how well each product is doing in the market. This includes looking at profitability, market share, customer feedback, and potential for growth. This assessment helps pinpoint which products are excelling and which may need to be adjusted or removed.
The next step involves aligning products with the company’s strategic goals. This ensures that each product contributes to the company’s main objectives, such as entering new markets, building brand strength, or adopting new technologies. Effective resource allocation is another key component of managing the product portfolio. This step involves making decisions about where to invest in development, where to expand, and where to reduce or cut back. Proper allocation helps optimize returns and supports the company’s strategic goals.
Finally, risk management is an essential part of the process, focusing on identifying and addressing potential risks related to the product portfolio. This includes handling market fluctuations, competition, and operational challenges to keep the portfolio adaptable and resilient.
In summary, Product Portfolio Management Analysis provides a framework for making informed decisions about product offerings, aiming to achieve a balanced and strategically aligned portfolio that promotes long-term success.
You can learn more about Portfolio Management Analysis Strategy through these sources :
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/portfoliomanagement.asp
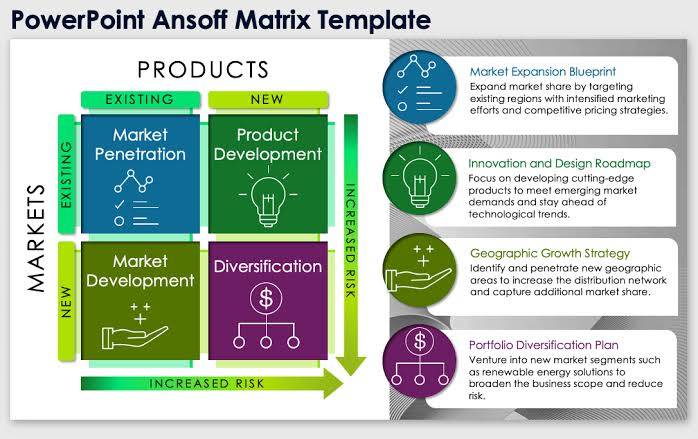
Igor Ansoff Model, Ansoff Matrix
Definition: The Ansoff Matrix is a strategic tool that helps businesses identify growth opportunities by analyzing potential combinations of new and existing products and markets.
Summary: The matrix outlines four strategies: market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification. It assists companies in evaluating ways to expand their operations, whether by boosting sales in current markets, entering new markets, creating new products, or exploring new business areas.
Business Model Canvas
Definition: The Business Model Canvas is a strategic tool that outlines and visualizes a company’s business model using a structured, one-page diagram. It captures key elements such as value propositions, customer segments, and revenue sources.
Summary: This canvas divides a business model into nine crucial components: customer segments, value propositions, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure. It helps companies map out their operations, understand their market positioning, and identify areas for improvement or innovation.
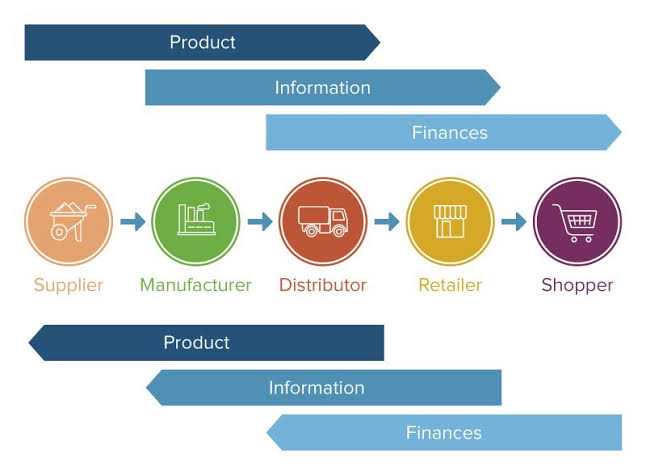
Lean Supply Chain Strategy
Definition: The supply chain is the entire system of processes and organizations involved in creating and delivering a product, from raw materials to the final consumer.
Summary: It includes activities such as procurement, production, logistics, and distribution. Managing the supply chain effectively helps streamline operations, reduce costs, and ensure timely delivery of products to customers.
supply chain management
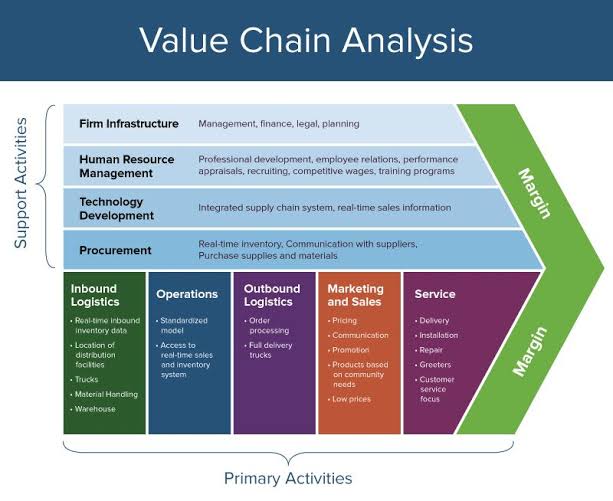
Value Chain Analysis in Strategic Management
Definition: The value chain is a model that describes the sequence of activities a company performs to produce and deliver a product or service, aiming to add value at each stage.
Summary: It divides activities into primary areas (like production and marketing) and support areas (such as technology and HR). This model helps companies analyze and improve each step to enhance overall efficiency and value for customers.
Others
Shewhart cycle
The Shewhart cycle, also known as the Plan–Do–Check–Act (PDCA) cycle, is a four-step process for continuous improvement in business:
Plan: Identify the problem or opportunity and create a plan to implement change
Do: Test the plan with a small-scale pilot project
Check: Analyze the results of the pilot project
Act: Implement the solution
The Shewhart cycle is based on the scientific method of problem-solving and combines management thinking with statistical analysis. It was originally developed by American physicist Walter A. Shewhart in the 1920s. Dr. W. Edwards Deming popularized the cycle in the 1950s and coined the term “Shewhart cycle” after his mentor.
The Shewhart cycle is a loop, not a process with a beginning and end. It’s similar to the Japanese business philosophy of Kaizen, and many large corporations have seen growth after implementing it.